Related Systems/Technologies/Research Projects (under construction)
Data-centricなものに関しては,Anhai Doan, Michael Franklin, Donald Kossmann, Tim KraskaらによるVLDB2011でのチュートリアルがあります.本プロジェクトにも触れられています.
- TurKit: A Java/JavaScript API for running iterative tasks on Mechanical Turk. With TurKit, programmers write programs in a straightforward imperative manner, but can safely re-execute programs without re-running costly side effects on Mechanical Turk. CyLog provides a data-centric declarative abstraction, focusing on the fusion of human/machine computations.
- CrowdLang: A model-based programming language for complex crowdsourcing applications.
It is interesting that it provides a set of common patterns and concepts taken from collective intelligence applications.
Currently, it seems that the codes in CrowdLang are written at an abstract level. In contrast, the codes in CyLog is executable.
- Collective Knowledge Bases:
In the project, they constructed a system to leverage mass collaboration to build large knowledge bases. In the system, contributers (1) give facts and rules and (2) receive feedbacks.
The collected knowledge base is utilized in an traditional expert-system fastion.
For example, it is used for printer truble shooting.
In contrast, CyLog is designed for data-centric applications, in which we collect, process, integrate, and manage data in the presence of human data sources.
This makes a big difference in the language design.
For example, CyLog does not take the traditional closed world assumption and has a mechanism to solicit human input.
- Qurk:
Qurk helps users build crowd-powered data processing workflows using a SQL-like language.
In Qurk, user-defined functions are incorporated into SQL queries to interact with the crowd.
In contrast, CyLog programs employ Datalog-style rules and an event-driven semantics.
- sCOOP: The Stanford--Santa-Cruz Project for Cooperative Computing with Algorithms, Data and People. Their hQuery is discussed in a Datalog-like notation. The h/ha-predicates of hQuery and our open predicates have some similarity. An open predicate is evaluated by humans when it cannot be evaluated by machines (through data or algorithms), while h-predicates and ha-predicates are evaluated by humans and both of human and algorithms, respectively.
It is interesting that they have different (and possibly complementary) approaches to deal with data values obtained by people.
hQuery takes the crowd-as-a-data-source approach, in that each value (associated with its certainty) is automatically by the crowd. They propose to use probability thresholds for that purpose.
In contrast, CyLog takes the human-as-a-data-source approach in that we model each human as a rational data source and that we design data games and aggregations to obtain values with required properties.
- CrowdDB: CrowdDB provides an SQL-compatible language to handle queries that cannot be answered by machines only. They try to achieve the data independence and query optimitzation in the presence of the crowd processing.
Their CNULL and our open attributes are similar to each other.
- CrowdForge: A MapReduce-like framework/toolkit, being developed by CMU, to implement complex crowdsourcing applications based on the partition, map, and reduce abstractions. Compared to CyLog, CrowdForge gives us a higher-level abstraction to define the structure of crowdsourcing applications.
We think that CyLog can be used as an executable language into which the application definition by CrowdForge can be translated.
|
Publications/Talks
- Atsuyuki Morishima. CyLog/Crowd4U: A Case Study of a Computing Platform for Cybernetic Dataspaces (招待執筆).
Handbook of Human Computation, Springer, 2014. (to appear)(NEW!)
- Atsuyuki Morishima, Takanori Kawashima, Takashi Harada, Norihiko Uda, Ikki Ohmukai.
L-Crowd: A Library Crowdsourcing Project by LIS and CS Researchers in Japan (招待講演),
International Conference on Digital Libraries (ICDL2013), November 2013. (to appear)
(NEW!)
- Aoki Hideto, Atsuyuki Morishima. A Divide-and-Conquer Approach for Crowdsourced Data Enumerataion.
SocInfo 2013, November 2013. (to appear)(NEW!)
- 森嶋厚行. Crowd4U/L-Crowd: アカデミアによる高度クラウドソーシングプラットフォームと図書館情報分野への応用 (招待講演).
第45回ディジタル図書館ワークショップ/情報処理学会第112回情報基礎とアクセス技術研究会合同研究会,2013年9月26日(NEW!)
- Kenji Gonnokami, Atsuyuki Morishima, Hiroyuki Kitagawa. Condition-Task-Store: A Declarative Abstraction for Microtask-based Complex Crowd-sourcing.
DBCrowd 2013: 20-25, August 2013.(NEW!)
- 森嶋厚行. Crowd4U: アカデミアと応用分野専門家が構築する高度クラウドソーシングプラットフォーム (招待講演).
第27回人工知能学会全国大会,2013年6月5日
- 丹治寛佳,森嶋厚行,井ノ口宗成.「Web情報を用いた災害状況把握のためのクラウドソーシング用マイクロタスクの試み」
2013年電子情報通信学会 総合大会講演論文集,1page, 岐阜大学,2013年3月19日.
- 富田栞,森嶋厚行,川島隆徳,宇陀則彦,原田隆史.「クラウドソーシングによる書誌誤同定発見のためのタスク設計」
2013年電子情報通信学会 総合大会講演論文集 ,1page, 岐阜大学,2013年3月19日.
- 青木秀人,森嶋厚行,三津石智巳.「クラウドソーシングによるデータ収集のためのタスク生成手法の提案」
第5回データ工学と情報マネジメントに関するフォーラム(DEIM 2013),7 pages, 福島県郡山市,2013年3月4日.
- 権守健嗣,森嶋厚行.「宣言的記述によるクラウドソーシングシステムの開発支援」
第5回データ工学と情報マネジメントに関するフォーラム(DEIM 2013),8 pages, 福島県郡山市,2013年3月4日.
- 三津石智巳,森嶋厚行,青木秀人.「Crowdsourced Join Pre-filterによるHuman-powerd Join処理効率化の評価」
第5回データ工学と情報マネジメントに関するフォーラム(DEIM 2013),8 pages, 福島県郡山市,2013年3月4日.
- Tomomi Mitsuishi, Atsuyuki Morishima, Norihide Shinagawa, Hideto Aoki. "Efficient Evaluation of Human-powered Joins with Crowdsourced Join Pre-filters." The 7th ACM International Conference on Ubiquitous Information Management and Communication (ACM ICUIMC2013), 6 pages, Kota Kinabalu, Malaysia, January 17-19, 2013.
- Atsuyuki Morishima. Declarative Data-centric Crowdsourcing (招待講演), The 7th Korea-Japan Database Workshop 2012,(KJDB 2012) November 30 - December 2, 2012.
- 森嶋厚行.「クラウドソーシングという新たな潮流に触れて」(招待講演), 第14回図書館総合展, パシフィコ横浜,神奈川県,2012年11月22日.
- Atsuyuki Morishima, Norihide Shinagawa, Tomomi Mitsuishi, Hideto Aoki, Shun Fukusumi. CyLog/Crowd4U: A Declarative Platform for Complex Data-centric Crowdsourcing, PVLDB 5(12): 1918-1921 (2012) (Demo page)
- 福角駿,森嶋厚行,品川徳秀,北川博之
「DB抽象化とゲーム理論に基づくマイクロブログからの構造データ抽出GWAPの開発」 (Applying DB Abstraction and Game Theory to Development of a GWAP for Extracting Structured Data from Microblogs)
DBSJ論文誌, Vol 11, No. 1, pp. 19-24, 2012年6月.
- 三津石智巳,森嶋厚行,品川徳秀,青木秀人
「Human-powered Join処理に対するクラウドソーシングを用いた効率化手法の評価 (Evaluation of a Crowdsourced Method for the Efficient Processing of Human-powered Joins)
第3回ソーシャルコンピューティングシンポジウム (SoC 2012), 6 pages, 東京,2012年6月.
- 三津石智巳,森嶋厚行,品川徳秀,青木秀人
「クラウドソーシングによるHuman-powered Joinの効率化
第4回データ工学と情報マネジメントに関するフォーラム(DEIM 2012), 6 pages, 神戸,2012年3月.
- 福角駿,森嶋厚行,品川徳秀
「GWAPによるマイクロブログからの構造データ抽出」
第4回データ工学と情報マネジメントに関するフォーラム, 8 pages, 神戸,2012年3月.
- 青木秀人,森嶋厚行,品川徳秀,三津石智巳
「データ中心型クラウドソーシングのための網羅演算の提案」
第4回データ工学と情報マネジメントに関するフォーラム(DEIM 2012), 7 pages, 神戸,2012年3月.
- Atsuyuki Morishima, Norihide Shinagawa, Shoji Mochizuki. The Power of Integrated Abstraction for Data-centric Human/Machine Computations. First International Workshop on Searching and Integrating New Web Data Sources (VLDS2011) Co-located with VLDB 2011, pp. 5-9, September, 2011. (pdf here. Slides here.)
- 三津石智巳,品川徳秀,森嶋厚行, (研究協力者: 望月祥司,安永ゆい,山口佳祐,青木秀人).「人と計算機の知の融合アプリケーションとその開発環境」.第2回ソーシャルコンピューティングシンポジウム (SoC2011), 2011年6月. (poster with demonstrations: poster in Japanese here)
- 三津石智巳,望月祥司,森嶋厚行「人と計算機を情報資源とする統合情報検索システムCySearchの提案」
情報処理学会第73回全国大会講演論文集(第1分冊), pp. 683-684, 2011年3月.
- 安永ゆい,望月祥司,森嶋厚行「GWAPによるオントロジ構築手法の提案」
情報処理学会第73回全国大会講演論文集(第1分冊), pp. 765-766, 2011年3月.
- 森嶋厚行「人と計算機の知の融合のためのプログラミング言語と開発環境」
合同エージェントワークショップ&シンポジウム2010 (JAWS2010), JSTさきがけセッション, 2010年10月27日-29日
- Atsuyuki Morishima. A Database Abstraction for Data-intensive Social Applications.
The 5th Korea-Japan Database Workshop 2010 (KJDB2010), May 28-29, 2010.
Jeju Province, Korea. (Invited Talk: Slides here)
- Atsuyuki Morishima, Noriaki Anzai. A Database Language for Collaborative Data Management by Computers and People. IPSJ Technical Report, 2009-DBS-149(12), pp. 1-8, Nov. 2009. (in Japanese)
|

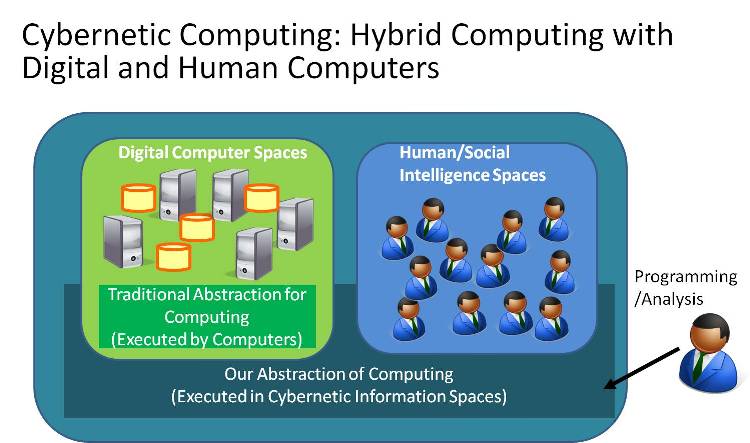 FusionCOMPプロジェクトの中心課題は,人と計算機の知の融合を記述する,実行・解析可能なアブストラクションとしてのプログラミング言語の研究です.
その研究を通じて目指す目標は,大きく二つに分けられます.
FusionCOMPプロジェクトの中心課題は,人と計算機の知の融合を記述する,実行・解析可能なアブストラクションとしてのプログラミング言語の研究です.
その研究を通じて目指す目標は,大きく二つに分けられます.